The Role of Blast Solutions in Construction
Blast-resistant modular buildings are essential to safely working in petrochemical facilities and other locations with blast hazards. These explosion-proof buildings with the appropriate psi ratings protect personnel and equipment during an incident.
Safety programs are a critical part of every operation, and it’s up to management to make sure employees take them seriously. One way to do this is to reinforce safe behaviors with positive outcomes.
Safety
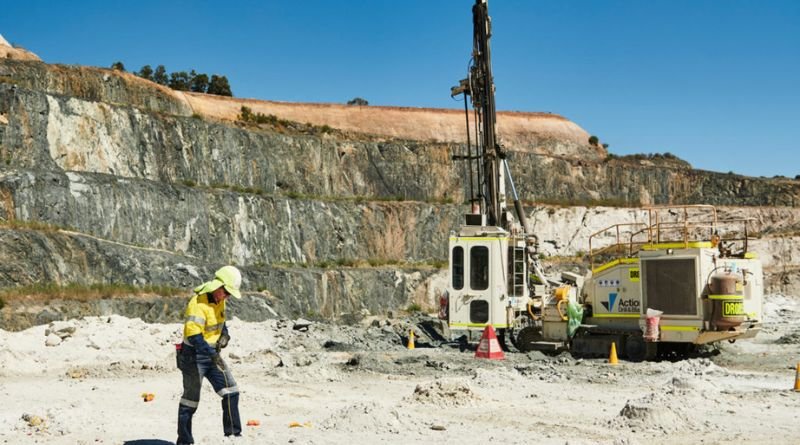
Blast solutions like the Airblast AFC Media Blast can enhance safety on construction projects through careful planning, risk assessment, and blast containment. Safety measures include ensuring minimal local disruptions and workers handling explosive materials are prequalified to follow blasting safety requirements.
Additionally, blast control components such as blast mats catch stray projectiles and debris, helping keep workers and bystanders safe from injuries. Using abrasive blasting materials can create dust clouds that threaten to contaminate the air on a job site and cause health risks for those in the surrounding area. To avoid this, it is recommended to use blast cabinets for smaller jobs or wet blasting when possible.
Modular buildings designed to withstand explosions can also help keep workers safe in the event of an accident. The hazard rating for these buildings is often misunderstood, with people thinking that higher numbers mean the building will withstand a larger blast pressure. However, it is important to understand that the number represents the duration of the blast (measured in seconds) while the impulse is measured in psi-msec.
Efficiency
Blasting can be a noisy, dusty job. Limiting the blast radius to the area that needs to be blasted is important. This helps avoid collateral damage. It also prevents the blast from damaging structures or equipment too close to the work zone.
When it comes to blasting, the blast specifications that the engineers write play a key role in the effectiveness of the project. They can dictate whether a particular type of abrasive is needed and if wet blasting is more effective than dry blasting.
The design of the structure is another consideration. The structure should be able to protect against both blast overpressure and projectiles, which requires extra engineering.
Productivity
Using abrasive blasting requires workers to spend time loading and measuring. That’s unproductive. But the right blasting equipment can save valuable worker time. Using pneumatic timers hooked to the deadman controls blast timing and increases productivity and efficiency.
A blast site’s location can also be an obstacle to productivity. Many municipalities have rules and regulations about where blasting can take place. It can be challenging to prove to the public that blasting will not impact their safety or environment.
Blast-resistant buildings may need to be designed with smaller windows to protect against higher psi blast ratings. This is especially true for areas like a factory’s alkylation unit, which can contain toxic gases or high-pressure pipelines. Keeping tools closer to employees reduces the amount of travel that exposes them to hazards. That can save valuable employee time and money throughout a shift. The cost savings can even pay for the building itself.
Environmental Impact
While blasting destroys surface material, it also helps stabilize the surrounding land. This is especially important on refinery sites where erosion is a significant problem. By quickly delivering a rock, the byproduct of our blasting, to the site, our customers can prevent land degradation and save on expensive erosion control costs.
Workers must be kept safe from the explosives when blasting occurs on job sites. Dry blasting creates dust clouds that can travel far from the shooting area, so safety equipment is critical. A self-contained breathing apparatus is necessary for all blasters, as are face shields and helmets to protect against flyrock.
Blast-resistant buildings must have electrical power, communication connections for LAN or WAN networks, and plumbing. Identifying these requirements early in planning will help ensure cost certainty and availability.